- Updated on August 3, 2019
![]() By Dr. Artour Rakhimov, Alternative Health Educator and Author
By Dr. Artour Rakhimov, Alternative Health Educator and Author
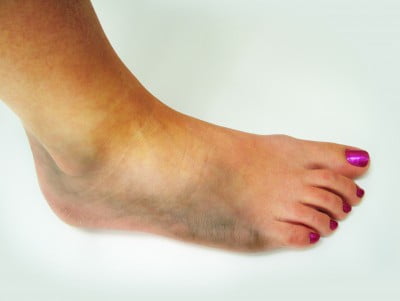 Swelling (medical terms: tumefaction or turgescence) is an abnormal enlargement of body cells usually due to inflammation. The inflammatory response is based on reactions of the immune system to tissue injury, but it can also take place due to other causes, such as tissue hypoxia and an allergic reaction that can target specific body areas.
Swelling (medical terms: tumefaction or turgescence) is an abnormal enlargement of body cells usually due to inflammation. The inflammatory response is based on reactions of the immune system to tissue injury, but it can also take place due to other causes, such as tissue hypoxia and an allergic reaction that can target specific body areas.
During the inflammatory response due to injury or caused by the allergic reaction, the immune system sends, via blood, white blood cells including neutrophils to release free radicals. These free radicals include reactive oxygen- and reactive nitrogen species that are supposed to destroy damaged cells and possibly pathogens that can be present in the site of injury. Released free radicals are effective in the destruction of cells and pathogens due to their ability to “borrow” electrons from other molecules and change their properties.
These are all useful effects related to the inflammatory response.
The key problem with this picture is that free radicals also diffuse into surrounding healthy cells and destroy them. This leads to the five classic signs of inflammation: redness, pain, immobility (or loss of function), heat and swelling.
However, according to recent clinical research, this abnormal scenario take place only when the human organism is ungrounded or electrically insulated from the Earth.
When the human body is grounded, the net body charge is negative. This means the presence of free electrons with a nearly unlimited supply of electrons from the Earth. As a result of grounding, the inflammatory response follows a totally different scenario: free radicals are able to attack only damaged cells and bacteria. There is no damage to healthy tissues and no redness, pain, immobility, swelling, or heat.
Worldwide, virtually all major surgeries are done on grounded people. This means that before the scalpel of the surgeon touches the human body, the body gets electrically connected to the Earth. Why? Decades ago, it was experimentally found that a lack of grounding, especially in the severely sick people, often leads to inflammation, while the whole surgery becomes dangerous due to complications related to inflammation. When the body is grounded, the inflammatory effect does not take place.
Wild animals, who are grounded 24/7, do not suffer from swelling and numerous inflammatory conditions, such as diabetes, arthritis, inflammatory GI problems and dozens of other inflammation-related illnesses (or these problems are very rare). However, domestic dogs, cats, and other insulated animals routinely develop nearly the same set of inflammatory diseases, often accompanied by swelling, when they adopt the modern ungrounded lifestyle.
Causes of chronic swelling
Swelling is dramatically worsened and becomes chronic due to poor circulation. This is a known medical fact. However, doctors generally do not know the cause of reduced blood supply that promotes swelling.
Another key factor that makes swelling chronic is tissue hypoxia. Water moves across various body surfaces passively following the laws of dilute solutions. If some parts of the body or cells have increased osmolarity, more water will be drawn to this area. Abnormally increased osmolarity of certain areas takes place due to ineffective work of tiny ionic pumps, which are responsible for active transport of various chemicals across cells and epithelial layers.
Now we are going to consider the key cause of reduced blood flow and decreased tissue oxygenation in the contemporary population. In other words, we are going to find the causes of why swelling often becomes chronic. Blood flow and perfusion of organs and tissues, as well as tissue oxygenation, are mainly controlled by breathing. Let us review clinical evidence related to changes in breathing rates during recent decades.
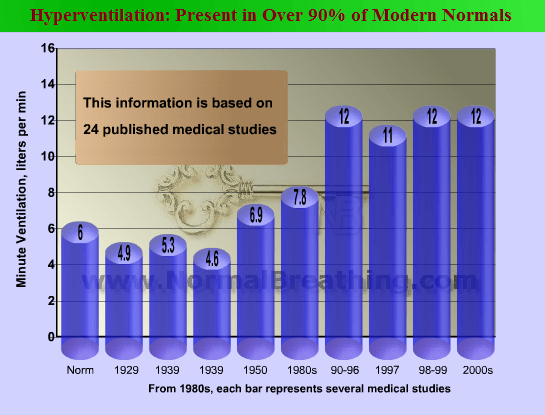
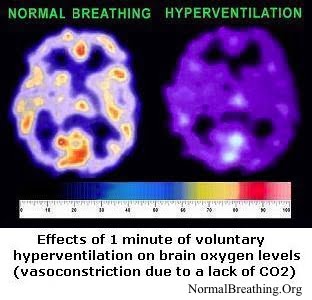 Since modern people breathe about twice more air than the medical norm, they suffer from chronic hyperventilation, which reduces blood flow and O2 transport to swelled tissues. Hyperventilation has a double negative effect: reduced circulation and tissue hypoxia, which suppresses ionic pumps that move chemicals across cells.
Since modern people breathe about twice more air than the medical norm, they suffer from chronic hyperventilation, which reduces blood flow and O2 transport to swelled tissues. Hyperventilation has a double negative effect: reduced circulation and tissue hypoxia, which suppresses ionic pumps that move chemicals across cells.
It is common for many modern men and women, especially with chronic health problems, inflammation, and swelling, to have less than 20 s for the DIY body-oxygen test (see test-related links below) due to overbreathing. The medical norm for this test is about 40-50 seconds, and normal subjects in the past had normal breathing parameters with over 40 s for the body-oxygen test.
How to reduce swelling
1. Grounding (also known as “Earthing“) can prevent swelling in the first place. It is also effective to reduce existing inflammation. See “How to ground yourself” for more detail.
2. In order to deal with already existing swelling, a person needs breathing retraining in order to normalize blood flow and body oxygenation. Learn how to practice Buteyko reduced breathing exercises.
Many traditional official medical approaches to reduce swelling are also based on similar ideas: application of oxygen and (artificial) attempts to improved blood flow.
According to the clinical experience of over 200 Russian medical doctors, mainly family physicians, swelling, and inflammation naturally disappear, when their patients start to slow down their automatic breathing patterns. The first signs of reduced swelling can be observed after a single 20 min breathing session. The main positive effects often take place within days.
It is often sufficient to achieve over 30 s for the body O2 test 24/7 in order to reduce or eliminate swelling completely. However, certain health conditions with inflammation and swelling require over 40 s 24/7 for the body-oxygen test to get rid of swelling completely.